Scientific Publication
Identifying Double Bond Positions in Phospholipids
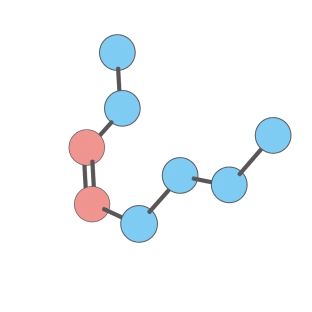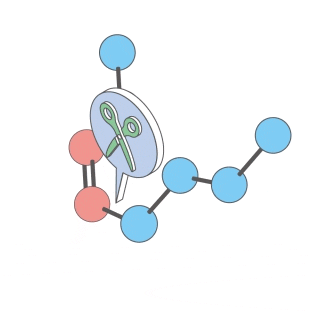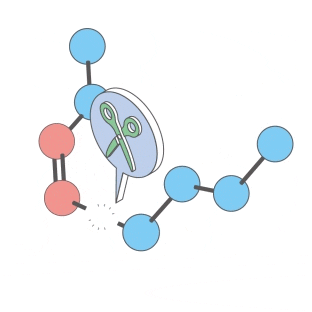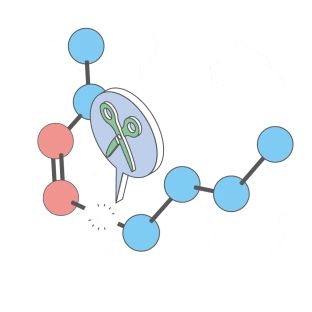
Oxygen Attachment Dissociation (OAD) is an ion dissociation technology developed by Shimadzu (patented), that enables an easy estimation of the position of double bonds within a carbon chain.
OAD Technology was developed at the Koichi Tanaka Mass Spectrometry Research Laboratory which target mass spectrometry-based solutions to help advancing research in healthcare and Life Sciences fields, Food technologies, Cosmetics, etc.
As an example, The function of lipids differs depending on the presence of double bonds between carbon atoms and their positions. In that scope, OAD technology will be of great help to elucidate the structure and differentiate them.
The OAD fragmentation box can be easily installed on your Q-TOF system as an add-on. You can then switch between the two fragmentation CID and OAD technologies.
They are complementary and work in positive and negative mode
Acquisition of a large amount of structural information by OAD and CID can lead to new discoveries in lipid analysis and other organic compounds.
The OAD-TOF system can be used in combination with various options compatible with the LCMS-9050:
DPiMS-QT ion source for quick analysis without pre-treatment
For quick analysis without sample pre-treatment
SICRIT ion source for LC/SFC/GC coupling
SFC chromatography
Isomers with similar structures can be completely separated by SFC
Scientific Publication
Identifying Double Bond Positions in Phospholipids
Scientific Publication
Computational mass spectrometry accelerates C = C position-resolved untargeted lipidomics using oxygen attachment dissociation
Scientific Publication
Structural Analysis of Phospholipid using HAD and OAD